SEO Glossary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| SEO | SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the process of optimizing on-page and off-page factors, so that a website becomes easier for search engines to crawl and rank in the organic, or free, search engine results. The higher a website ranks in the search results for a relevant keyword, the more website visitors and conversions a website will receive. |
| Search Engine | Google, Yahoo and Bing are all search engines (SEs). They use sophisticated algorithms to serve users’ queries in the most efficient and relevant way. |
| Search Engine Bot | Search engines use computer programs called robots, or bots, to crawl web pages – both the millions of new ones that appear every day and the ones that are updated and need to be re-crawled. |
| Search Engine Algorithm | Back in the early ages of the internet, the search engines used to rank web pages manually. That is a human had to choose which page holds #1 position and so on. The Google founders quickly realized there needed to be a way to rank sites automatically, which is when they developed a Search Engine Algorithm which ranked sites based on the references, or backlinks, it received from other sites. If a large number of sites talk about the same topic, the site which has the most backlinks will receive the top position within the search engine result page and, therefore, receive the most clicks. This basic rule is referred to as PageRank. From this point on, Google and other search engines constantly improved their Search Algorithms so that they best serve user’s queries. |
| RankBrain | RankBrain is an artificial intelligence (AI) program used to help process Google search queries. RankBrain is currently trying to match new, never before seen queries to familiar keywords or phrases and display results based on these synonyms. |
| Google Updates | Google is constantly updating its search algorithm to fight web spam and some of these updates impact millions of sites directly. Following Google Webmaster Guidelines will prevent your site from being penalized by Google. Two of the most impactful Google updates are:
|
| Search Query | This is the query (keyword or phrase) that a user enters into a search field to satisfy their need of information. When optimizing a web page, it is important to have an idea of what the searcher’s query might be. |
| SEM | SEM (Search Engine Marketing) is a way to promote your site via the search engines, primarily through paid advertising. SEM can be used for promoting products to a user who is actively searching for them. SEM is not recommended for new, unknown products which are just entering the market. These products are easier to advertise via social networks where a specific target group can be reached. |
| PPC | PPC (Pay Per Click), also known as CPC (Cost Per Click) is a SEM model in which an advertiser pays a publisher (typically a search engine) when an ad is clicked. It differs from pay per view or pay per impression types of advertising (e.g. 1000 impressions of a banner) because there is an action (interest) from the user and is therefore more effective. |
| Conversions | A website conversion takes place when a visitor to your site performs an action that is valuable to you. This action can be clicking a button, filling in a contact form or making a purchase. |
| Page Title | A page title is used in a SERP within the result snippet. The title has a larger font size and is one of the things users skim through when choosing on which result to click. The page title should show what the main topic of the page is and the desired keyword to rank for. It is an important on-page ranking factor and should be treated with care. Here’s what the page title looks like in HTML:Expert search engine optimization drives traffic, leads, conversions and ROI. | The Search Guru 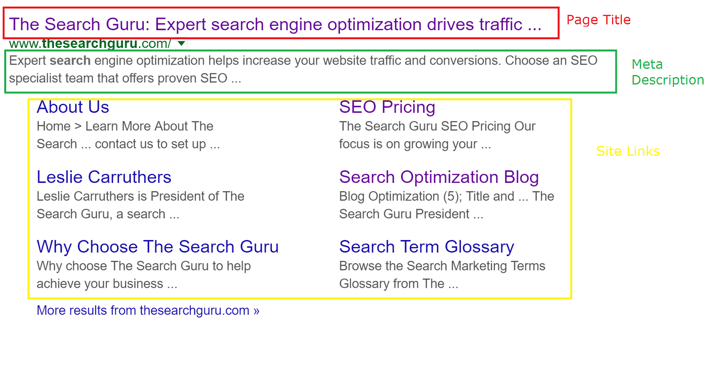 |
| Meta Description | The meta description is also shown within the SERP result snippet. Though it is not a ranking factor, it is a way to advertise your content and increase click-through rate. The meta description is an HTML tag with a recommended length around 160 characters. Here’s how the meta description looks in HTML: |
| Domain Authority | Domain authority is a score (ranging from 0 to 100) developed by Moz.com which tries to predict how well a website will rank within search engines. Domain authority can be used to compare one site to another or can track the “strength” of a website over time. The number and strength of backlinks to a domain is the main factor for domain authority. |
| Page Authority | Page authority is a score (ranging from 0 to 100) developed by Moz.com which tries to predict how well a single web page will rank within search engines. |
| Backlinks | Backlinks are the most important factor for ranking a web page in the SERPs. Having another webmaster refer to your site is a signal to the search engines that your site is valuable. It is not only the number of the links that matter, but also the quality and relevancy of those links. |
| Link Scheme | Any link which is intended to manipulate a site’s ranking within the search results may be considered part of a link scheme and a violation of Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. Taking part of link scheme tactics may lead to penalties and a de-indexing from Google’s results. |
| Conversion Rate | Conversion rate is the percentage of converted visitors compared to total visitors. An e-commerce conversion rate of 1.5% to 2.0% is considered average. |
| Click-Through Rate | Click-through rate (CTR) is the percentage of clicks vs. impressions, or the visits to a page vs. the number of times the page was shown in the SERPs. |
| Click | A click to your site is counted when a visitor searches for something and comes to your site. For PPC ads, when there’s a click to your site, you are charged by the search engine. |
| Impression | Impressions are the number of times your page has been shown to users in the SERPs. Impressions for PPC ads are used to calculate the CTR, which is a Quality Score factor. For organic results, impressions can be seen in the Google Search Console tool. |
| Quality Score | Quality Score (ranging from 1 to 10) is applied to keywords in AdWords campaigns. It is calculated from CTR, ad relevance, ad group relevancy, landing page relevancy and quality, and historical account performance. Optimizing your landing pages, ads and ad groups will lead to higher Quality Scores for your keywords, which means better ad positioning and lower bid prices. |
| SERP | SERP (Search Engine Result Page) is the page that displays with the results from a user’s search, which have been ranked for a specific user query. |
| Google Search Console | A free tool provided by Google. Once your site is verified within Google Search Console, it provides valuable information about how Google perceives your site, including certain types of issues and errors. |
| Google Analytics | A free tool that provides website and mobile application data reporting that analyzes your visitors’ behavior and can inform key business decisions. |
| Keywords | An SEO or PPC keyword refers to the actual term or phrase people use when searching. Ranking for the most popular or general keyword in your business area is usually challenging. That is why it’s important to identify other more specific and/or less general keywords to rank for (this process is known as keyword research). |
| Keyword Research | When looking for the best keywords for your website, you should select keywords that have a relatively good amount of searches per month (the Google Ads tool “Keyword Planner” shows the number of searches per keyword per month) and compare it to the chance of ranking for this keyword by evaluating the competition within the SERPs. This evaluation process is known as Keyword Difficulty. |
| Keyword Difficulty | Keyword Difficulty is a metric ranging from 1 to 100 which shows how competitive a search term is. The higher the keyword difficulty number is, the more competitive a term is and the harder it is to rank for it. Keywords with difficulty of below 30 are considered easy, between 31 and 70 – medium, and above 71 are thought of as hard to rank for. |
| Google Search Console | A free tool provided by Google. Once your site is verified within Google Search Console, it provides valuable information about how Google perceives your site, including certain types of issues and errors. |
| Long-Tail Keywords | Keywords of more than two words are referred to as long-tail keywords. They usually have lower search volume, but they might be even more relevant to your services and may also result in a higher conversion rate. |
| Crawl Budget | Google allocates a certain amount of resources to crawling a site based on the importance of a site, known as the crawl budget. For example, CNN.com has a larger crawl budget, and is more frequently crawled by Google bots for new updates, than a small personal blog. Therefore, websites should be structured to allow Google bots to crawl the most important pages first by placing them higher in the website hierarchy. |
